ES1 | Exploring Logic's E-Synths
Written by Matt Ho and Maya Wagner
Introduction
Welcome back to the wonderful world of synthesis! In this collection of posts, Maya and Matt explore where Logic all started with a comprehensive guide to Logic's E-synths!
Before Apple purchased Logic and rebranded it into what we know and love today, a company known as Emagic owned the license to the software. This is where the namesake “ES” or “E-synth” comes from. Since the rebrand, Logic has kept six of the original instruments from Emagic’s version of the Software. These synths have been kept intact without many updates or interface changes, honoring Logic’s sound design roots. Logic’s developers have an interesting way of maintaining the aesthetics of old plugins and synths while adding new “modern” ones to create an interesting smorgasbord of looks and feels. It's part of what gives Logic its character!
Today's post is about ES1, a powerful and versatile synthesizer that emulates those classic analog synthesizers of the 70s and 80s. One of the coolest but most advanced aspects of this synth is the modulation routing parameters, which makes this synth more advanced than our previous contestants, but much more powerful as a result! ES1 provides a fabulous bridge between the other "ES" models and the all-mighty ES2.
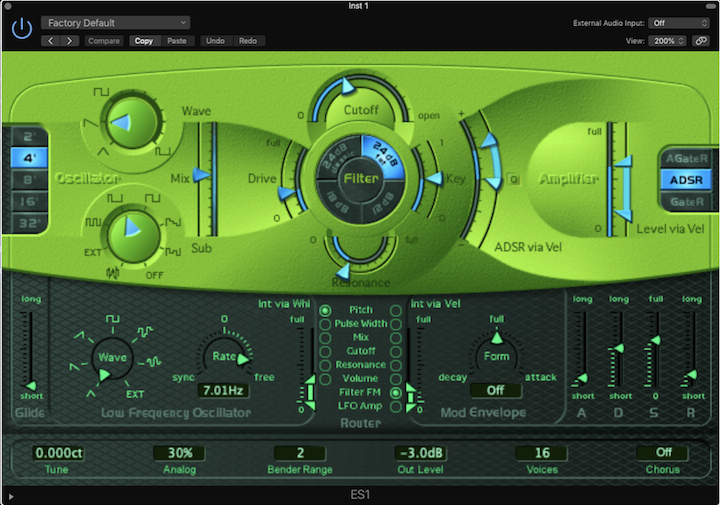
Quick Overview
Subtractive synth with 2 Oscillators (Mix), 1 Low Pass Filter (Adjustable Slope), 1 LFO, 1 Simple Modulation Envelope, and 1 Volume Envelope with ADSR Controls.
Controls
Level via Vel - Controls the maximum and minimum volume that the velocity maps to on the main output. Ranges from 0 (no volume) to FULL volume.
2, 4, 8, 16, 32 - Selects octaves for oscillators. Similar to organ conventions, longer pipes (2 < 4 < 8 < 16 < 32) goes into a lower octave.
Oscillators
Wave - Selects the wave shape of the main oscillator.
Sub - Selects the wave shape of the sub-frequency oscillator.
Mix - Controls the mix of the two oscillators’ signals.
Filter and Filter Slopes
Drive - Controls the input level of the filter, and affects the level of overdrive in the filter. Ranges from 0 (no drive) to Full.
Resonance - Controls the amplitude boost at the cutoff frequency. Ranges from 0 (no drive) to full.
Cutoff - Controls the cutoff frequency of the filter. Ranges from 0 (closed) to open.
Key - Controls the amount of key following applied to the cutoff frequency. Ranges from 0 (no key following) to 1 (full key following).
24 dB classic - Mimics the behavior of a Moog filter. Increase the Resonance parameter value to reduce the low end of the signal.
24 dB fat - Compensates for the reduction of low-frequency content caused by high Resonance values. This resembles the behavior of an Oberheim filter.
12 dB - Provides a soft, smooth sound that is reminiscent of the early Oberheim SEM synthesizer.
18 dB - Resembles the filter sound of the Roland TB-303.
Modulation Routing
LFO - Can choose between 7 different LFO waveforms which can be set to modulate pitch, pulse width, cutoff, resonance, or volume (select these in the router and adjust LFO amount and range with the vertical sliders)
Mod Envelope - Can use the Attack/Decay envelope to modulate pitch, pulse width, cutoff, resonance, filter FM, LFO amplitude, or volume (select these in the router and adjust LFO amount and range with the vertical sliders)
Global Parameters
Glide - controls the length of time it takes one note's pitch to bend to another (when completely short, no glide).
Tune - Detune the output by cents
Analog - this parameter changes the pitch and cutoff frequency ever-so-slightly to emulate the character of a hardware analog synthesizer
Bender Range - controls the sensitivity to pitch bend midi CC
Chorus - select either a classic chorus or ensemble or disable the effects:
Off disables the built-in chorus circuit.
C1 is a typical chorus effect.
C2 is a variation of C1 and is characterized by a stronger modulation.
Ensemble uses a more complex modulation routing, creating a fuller and richer sound
Applications and Uses
ES1 is a powerful subtractive synth. In examples such as the ES E, which is named "E" for "Ensemble," we have a clear idea of what the synth was meant to be used for: ensemble style instruments like pads, analog strings, and other textures.
However, with ES1, there is a lot more room for experimentation. ES 1 is a great synth for beginners to learn about modulation routing and parameters. Unlike the other ES instruments in Logic (save ES2), ES1 has a modulation routing system that allows generators (envelope and LFO) to control different parameters rather than just controlling pitch. This allows for a world of sound design opportunities! Play around with the mod engine and see what you can do!

