ESFM1 | Exploring Logic's E-synths
Written by Matt Ho and Maya Wagner
Introduction
Before Apple purchased Logic and rebranded it into what we know and love today, a company known as Emagic owned the license to the software. This is where the namesake “ES” or “E-synth” comes from. Since the rebrand, Logic has kept six of the original instruments from Emagic’s version of the Software. These synths have been kept intact without many updates or interface changes, honoring Logic’s sound design roots. Logic’s developers have an interesting way of maintaining the aesthetics of old plugins and synths while adding new “modern” ones to create an interesting smorgasbord of looks and feels. It's part of what gives Logic its character!
Today's post is about EFM1, a simple but mighty frequency modulation (FM) synth. FM synthesis is the process of modulating one waveform (the carrier) with another (the modulator) to create a new waveform. FM synthesis was discovered by legend John Chowning in 1967 and his innovation was licensed by Yamaha, who created the massively popular DX7!
FM synthesis creates a unique harmonic series that is extremely useful for creating bell-like sounds but can be used to create tons of cool "digital-sounding" patches.
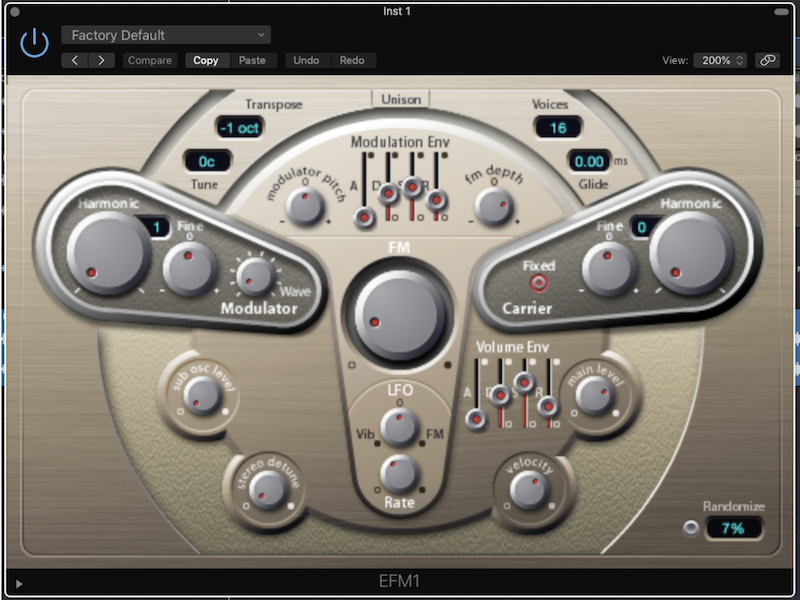
Quick Overview
Frequency Modulation (FM) Synth with 1 Carrier Oscillator, 1 Modulator Oscillator, 1 Sub Oscillator, 1 LFO, 1 Volume Envelope with ADSR Controls, and 1 Modulator Envelope with ADSR Controls.
Controls
Transpose - Select the base pitch for your oscillator. Ranges from -2 Octaves to +2 Octaves (in increments of semitones).
Tune - Controls the fine-tuning of the synth by cents. Ranges from -50 cents to +50 cents
Voices - Selects the number of notes that can be played at the same time. Ranges from legato, monophonic, and polyphonic (up to 16).
Unison - Layers a double of the set of notes played (thus thickening the sound). Enabling this will limit the number of polyphony to a maximum of 8.
Glide - also known as portamento, controls the time it takes for the synth to glide/bend into the next note if they are played legato. Range - Low (0%) to High (100%).
Carrier Oscillator
Fixed - Enables/Disables the pitch of the carrier oscillator to follow the MIDI note input.
Fine - Controls the tuning of the Carrier oscillator relative to the Modulator tuning.
Hamonic - Selects the harmonic that the Carrier oscillator is tuned to. Ranges from 0 (off) to fundamental (1) to 36. Note that when the Carrier oscillator is off, and both FM and FM depth is set to 0, there will be no sound produced.
Velocity - Controls the velocity sensitivity on the output volume
Main Level - Controls the Volume at the output
Modulator Oscillator
Wave - Selects the wave shape of the Modulator Oscillator. Sine wave selected when the knob is set hard left.
Fine - Controls the tuning of the Modulator oscillator relative to the Carrier tuning.
Hamonic - Selects the harmonic that the Modulator oscillator is tuned to. Ranges from 1 (fundamental) to 36.
Modulation Envelope
Modulator Pitch - Controls the Amount (depth) of modulation from the modulation envelope affecting the pitch of the modulator. Ranges from -100% to 0 (no modulation) to 100%.
FM depth - Controls the Amount (depth) of modulation from the modulation envelope affecting the FM intensity of the modulator. Ranges from -100% to 0 (no modulation) to 100%.
A - Controls the Attack time of the modulation envelope
D - Controls the Delay time of the modulation envelope
S - Controls the Sustain level of the modulation envelope
R - Controls the Release time of the modulation envelope
LFO
Vib-FM - Controls the Amount (depth) of modulation from the LFO affecting either Vibration (pitch) or intensity of FM. Ranges from 100% Vibrato (LEFT) to No Effect (Centre) to 100% FM (Right).
Rate - Controls the cycle of oscillation of the LFO. Ranges from SLOW to FAST.
Sub Osc Level - Controls the volume of the Sub frequency (-1 octave) sine oscillator going to the output. Ranges from Off to Full Volume.
Stereo Detune - Controls the amount of detuning applied to the L+R output.
Volume Envelope
A - Controls the Attack time of the volume envelope
D - Controls the Delay time of the volume envelope
S - Controls the Sustain level of the volume envelope
R - Controls the Release time of the volume envelope

